Introduction to Cryogenic Valves: The Ultimate Guide

Cryogenic valves are specialized devices designed to operate in extremely low-temperature environments, typically below -40°C, and are crucial for the safe and efficient handling of cryogenic liquids and gases. These valves are essential in industries such as petrochemicals, natural gas, healthcare, and manufacturing, where they play a pivotal role in gas liquefaction, separation, transport, and storage. This comprehensive guide explores the key aspects of cryogenic valves, including their operation, selection criteria, types, and the latest innovations.
The Need for Cryogenic Valves
The liquefaction temperatures of various substances necessitate the use of cryogenic valves:
- Liquid ammonia: -269°C
- Liquid hydrogen: -254°C
- Liquid helium: -196°C
- Liquid oxygen: -183°C
- Liquefied natural gas: -162°C
These valves are essential for the fractional distillation, transportation, and storage of these substances. Applications include ethylene and LNG plants, LPG and LNG storage tanks, receiving bases, satellite stations, air separation equipment, petrochemical tail gas separation equipment, low-temperature storage tanks for liquid oxygen, nitrogen, argon, carbon dioxide, and cryogenic tankers.
Choosing the Right Cryogenic Valves
Selecting the appropriate cryogenic valve involves considering several critical factors:
Temperature Range
Cryogenic valves must be capable of withstanding extremely low temperatures without compromising their integrity. Common cryogenic temperatures include:
- Liquid Oxygen: -183°C
- Liquid Nitrogen: -196°C
- Liquid Natural Gas (LNG): -162°C
- Liquid Helium: -269°C
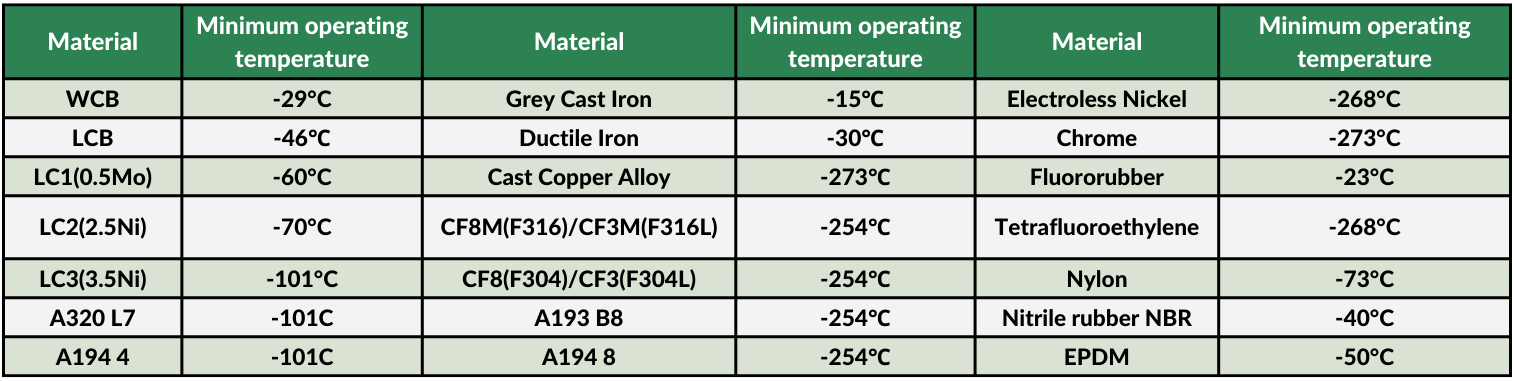
Material Selection
Materials used in cryogenic valves must maintain their mechanical properties at low temperatures. Key materials include:
- Austenitic Stainless Steel: Suitable for temperatures below -100°C, offering excellent corrosion resistance and toughness.
- Nickel Alloys: Ideal for applications involving liquid helium or hydrogen, providing superior performance at temperatures as low as -253°C.
- Ferritic Steels: Used for less extreme temperatures, typically above -100°C.
Design Considerations
Cryogenic valves often feature a higher packing part and an extended stem to reduce heat transfer from the outside to the inside of the device. The long-neck bonnet design is another crucial element, minimizing heat dissipation and ensuring efficient operation.
Leakage Prevention
Preventing leakage is paramount in cryogenic systems. Look for valves with robust sealing mechanisms, such as metal-to-metal seals or elastomeric seals, to ensure reliable performance and safety.
Certification and Standards
Ensure the valves comply with industry standards and certifications, such as API 6D, BS 6364, and ISO 21011, which specify requirements for cryogenic service and safety devices.
Types and Differences of Cryogenic Valves
Cryogenic valves come in various shapes and sizes, each suited for different applications and pressure ranges. Common types include:
- Cryogenic Ball Valves: Feature a polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) body, offering better flow rates and tight seals. Ideal for systems with unrestricted flow paths.
- Cryogenic Globe Valves: Have a spherical shape and an internal moving disc, providing effective long-term sealing. Not recommended for high-flow systems.
- Cryogenic Gate Valves: Use a wedge-shaped gate, resulting in minimal pressure drop even in fully open positions.
- Cryogenic Butterfly Valves: Lightweight and economical, these valves have a circular disc in the center, suitable for systems needing fast opening and closing actions.
- Cryogenic Relief Valves: Protect against overpressure and allow steam to escape if safety limits are exceeded.
- Cryogenic Non-Return Valves: Maintain pressure and prevent fluid backflow.
Case Studies and Success Stories
LNG Storage Facility
An LNG storage facility implemented cryogenic ball valves made of austenitic stainless steel, improving operational efficiency and reducing maintenance costs.
Hydrogen Fueling Station
A hydrogen fueling station utilized nickel alloy globe valves to handle liquid hydrogen, ensuring safety and reliability in expanding the hydrogen refueling network.
Conclusion
Cryogenic valves are indispensable for the safe and efficient handling of cryogenic liquids and gases. By considering factors such as temperature range, material selection, design, leakage prevention, and industry standards, businesses can ensure the optimal performance of their cryogenic systems.
